Frequently Asked Questions About Iron Alloy
What are common uses for gray iron alloy?
Believe it or not, gray iron is widely used throughout the world, and it is one of the most popular metals. It can be found in manhole covers, wind turbines, cinder blocks, automotive suspension and hydraulics, gears, disc brakes, cooking utensils, valves, tractor parts, pumps, linkages, weights, counterweights, and so much more.
Why is gray iron so popular?
Gray iron is actually one of the cheapest iron alloys to produce. And thanks to its properties, such as its ductility and strength, many find it the perfect fit for any type of application.
What are the common uses for ductile iron?
Ductile iron alloy has many different applications due to its properties. It’s commonly used in piping, both in and out of the water, as well as component parts for cars and trucks, pump housing, drinking and potable water distribution and transmission, and so much more.
Is ductile iron the same as cast iron?
Ductile iron is a type of cast iron. In fact, some people refer to it as modern-day cast iron and have even referred to it as ductile cast iron. Both of these metals contain small pieces of graphite that end up changing the properties of the iron alloy. This likely explains why they are so similar. However, ductile iron is different from cast iron in that it is highly flexible and corrosion-resistant while cast iron is neither of these things.
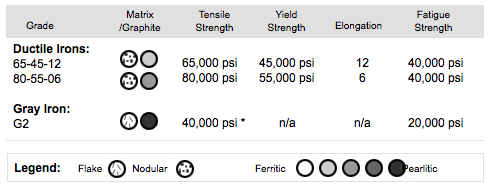
What’s the difference between gray iron and ductile iron alloys?
While both beautifully serve their purpose, there are a few differences between gray iron and ductile iron alloys. Knowing them will help you decide which may be the best choice for your application. Let’s take a look at how they stack up against each other:
- Ductility: Ductile iron has greater strength and ductility than gray iron
- Thermal conductivity: Gray iron has a higher thermal conductivity than ductile iron.
- Vibration dampening: Gray iron more effectively dampens vibrations than ductile iron.
- Tensile strength: Gray iron has a range of 20,000 psi to 60,000 psi and ductile iron has a minimum of 40,000 psi.
- Yield strength: Gray iron does not have a yield strength, but ductile iron has a range of 20,000 psi to 60,000 psi.
- Impact: Ductile iron has greater resistance on impact.
|